Send
, identify , trace Fake/Spoofed Email | Email Bombing | Email Spamming
Basics of working of Email
Email stands for Electronic Mail. Email
sending and receiving is controlled by the Email servers.Email service
providers configure Email Server before anyone can Sign into his or her
account and start communicating digitally.Users from across the
world register in to these Email servers and setup an Email account.
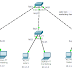
Email Travelling Path :-
Let’s say we have two Email providers, one is gmail.com and other is yahoo.com, ABC is a registered user in gmail.com and XYZ is a registered user in yahoo.com.
• ABC signs in to his Email account in gmail.com, he then writes a mail to the xyz@yahoo.com and sends the message.
• But what happens behind the curtains, the Email from the computer of abc@gmail.com is forwarded to the Email server of gmail.com. Server of gmail.com then looks for yahoo.com on the internet and forwards the Email of the yahoo.com for the account of XYZ@yahoo.com. Yahoo server puts that email in that account.
• XYZ then sits on computer and signs in to her Email account.Now she has the message in her Email inbox.
Sending Fake/spoofed Email -: Fake or spoofed email means the email from any email ID. It doesn't matter whether the sender's email really exists or not. Sender's email ID can be anything@anything.com.
Methods :-
1. Using Open Relay servers : An open relay server is that which allows people to send email by connecting to it. User connect to it via telnet and instructs server to send email. This method is outdated or simply I should say that, it doesn't work. I would not talk about it more.
2. Using Websites : There are numberless websites that provide free service to send fake emails. But the problem is that they attach the advertisments along with your email. But the best two, I have found that do not attach the advertisments.
www.emkei.cz {have some advance options}
www.hidemyass.biz/fake-mailer/
3. Using mail sending scripts : The PHP contains mail sending function which allows us to send email with fake headers.
Download a php script from here.
We just need to upload the mail sending script on a web hosting site. It doesn't work on every webshosting site because there is no email sending support. I have tested x10hosting.com (could take upto a day for account activation) , it works perfect. Some of the other are www.000webhost.com,byethehost5.com
Note: This script contains options of sending spoofed email, spamming and email bombing. Your hosting account might be immediately suspended on spamming/bombing. But it works perfect if you have any your own premium web hosting account. If you want to try email bomber, I could let you to use my own if sufficient people request in comments.
What is Email Spamming and Email Bombing ?
Email Bombing as clear from the name is
sending the mass emails that is large number of emails to a email ID in a
single click. Email spamming is like sending an email to large number of email
IDs in a single click. These activties are performed mainly for the
advertisements of the products or services provided by a company. Many spammers
spam to collect individual's personal information through some stupid things
like 'fill these details to get your lottery amount' and that information is
sold to businessmen looking for the people of different categories. There could
be many more reasons of spamming. Spammers use automated tools to collect as
many emails available on websites,forms,chat rooms and send spams to them.
How to identify whether an email is real or spoofed ?
It can be done by checking headers. Email headers is simply the text which contains the information about the mail servers that the email encountered in its path from the sender to receiver. It contains a lot of other information too.
Note: I am just telling you a few points about this so that you would just get an idea about the approach. This may or may not depend on some factors.
We can view email headers in gmail by clicking at 'show orignal', in yahoo by clicking at 'Full headers' and such kinds of options in other email service providers.
If you get an email displaying sender's email like someone@gmail.com, someone@hotmail.com, someone@yahoo.com . Then it should be orignated from gmail,hotmail and yahoo servers respectively. But if it doesn't, the most probably the email would be fake.
I will show you by an example, I received three emails in my gmail inbox from sender's address "someone@gmail.com." Sender's address shows me that they should have been orignated from gmail/google server, if they would be real.
Note : There is a field called "Return-path" in headers. If the email ID shown in this field and email ID you get as sender's email ID doesnt match, then the email is surely fake.
Can we get sender's IP
address from Email Headers ?
We may or may not. Gmail, yahoo normally do not reveal sender's IP address. But when we send an email from a php script, the headers might reveal Sender's IP. The conclusion is that answer to this question varies from different email service providers and the way how email is sent.
Can we trace sender's location, if we get his IP address ?
The IP address could only tell that which Internet Service Provider (ISP) is used by sender. Further details can not be revealed without the help of that ISP. Normally the Public IP is dynamic that is it keeps changing. We need to ask ISP about the user who was assigned that IP at the time email was sent. If sender has purchased a static IP address, it doesn't matter that when exactly was email sent. He could easily be traced.
We may or may not. Gmail, yahoo normally do not reveal sender's IP address. But when we send an email from a php script, the headers might reveal Sender's IP. The conclusion is that answer to this question varies from different email service providers and the way how email is sent.
Can we trace sender's location, if we get his IP address ?
The IP address could only tell that which Internet Service Provider (ISP) is used by sender. Further details can not be revealed without the help of that ISP. Normally the Public IP is dynamic that is it keeps changing. We need to ask ISP about the user who was assigned that IP at the time email was sent. If sender has purchased a static IP address, it doesn't matter that when exactly was email sent. He could easily be traced.









.jpg)



.jpg)








.jpg)