Network
Network is a telecommunications network that allows computers to exchange data. In computer networks, networked
computing devices pass data to each other along data connections. The connections
(network links) between
nodes are established using either cable media or wireless media.
• Towns and cities interconnected by roads and
motorways
• Computers exchanging data through cables
• People gossiping
Most experts agree that a computer network is formed
when two or more computers communicate. However, there are some people who insist that you need three computers
to make it a ‘real’ network.
Eg: LAN
WAN
CAN
Local Area
Network (LAN)
A LAN is a
computer network that interconnects computers within a limited areas using
network medias..
• School
• office network
Connections are made by copper or fibre-optic cable,
infrared or short-distance microwave radio
Wide Area
Network (WAN)
A WAN is a network that covers a broad area ( ie, any
telecommunication network that links across metropolitan,region,national.
.
.
• The telephone system
• A bank’s secure ATM (cash machine) network
• Satellite links between TV companies Connections are
made by copper or fibre-optic landlines, line-ofsight microwave radio, orsatellite
relay
Metropolitan
Area Network (MAN)
MANs connect
sites around a town or city.
• Town council offices
• University campus network
• Cable TV company
Connections are made by copper or fibre-optic
landlines, line-ofsight microwave or high-frequency radio
Other terms
Campus Area
Network (CAN): somewhere between a LAN and a MAN, this describes
connections over a village-sized area.
Usually restricted to larger universities.
Tiny Area
Network (TAN): used by some people to describe small networks within
a house or small office.
Topology
The study of geometrical properties and spatial
relation unaffected by the continuous change of shapr or size of figures.
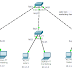
Star
In a star layout, all computers are connected to a
central hub. Star networks allow computers to be connected & disconnected
with ease, so long as enough ports are available. However, if the hub breaks then the entire
network goes down.
Ring
In a ring layout, each computer connects to two
neighbours to forma loop. Messages are
passed from computer-to-computer until they reach their destination. Ring
networks are efficient and cheap but if one of the computers breaks or is
removed then the entire network goes down.
Mesh
Mesh networks connect many computeers directly to each
other.This means faster communication, and provides alternative routes if a
computer or link breaks. However, more
connections means mesh networks are expensive to build.
Bus
A bus provides a common electrical connection for a
number of computers, but only two computers may communicate at the sametime
otherwise there will be a signal collision. Buses are very cheap and allow easy
connection & disconnection. However,
buses tend to slow down with increased message traffic.
Extended
Star (Tree)
The extended star design breaks the network into
smaller starconfigurations, each minor hub connected to a major hub. Extended stars offer an economical, modular
way of organising networks. They are
very common in modern network designs.
Relationships
A server program carries out work for client
programs.
Server software is often located on a powerful,
high-specification machine, allowing it to serve many clients at once. For this reason, the computer itself is
usually referred toas a server. A range
of server programs are available:
• File server: stores files centrally
• Print server: processes all printing for the network
and sends work to selected printers.
• Internet proxy server: connects to an ISP on behalf
of other computers on the network, passing messages to-and-from the Internet.
• Database server: allows simultaneous access to large
database files.
• Webserver: hands out webpages on request.
• Mail server: stores and processes email; like a post
office.
• Domain controller: this manages security for the
network, processing passwords and deciding who can access services.
•Client software is located on normal-specification
computers, known as workstations.
.
When a computer is capable of acting as both client
and server, we call it a peer.
Peer-to-peer networks contain computers that are requesting services from
each other.
Network Media
Electrical
media
Plain
copper wire
A pair of plain copper wires is a poor medium for
electronic signals, and is therefore rarely used in computer networking.
Electro-Magnetic
Interference (EMI): When a signal current passes
through a wire or circuit it creates small electrical and magnetic fields. These fields can affect signal currents in
other wires, or other circuits, adding electrical noise to the signals, degrading
them. Long, plain copper wires are easily affected by EMI — hence they should
not be used to carry computer signals more than a few of metres.
Co-axial
Cable (Co-ax)
In co-ax a copper wire is surrounded by a copper
screen. This screen (usually a fine
braid or mesh of copper filaments) is connected to signal ground and it absorbs
EMI, protecting the signal wire from electrical noise. Screen and signal wire are separated by
plastic insulation.
Bandwidth
The closeness of the screen and signal wire creates an
effect called capacitance. This limits
the range of frequencies — bandwidth — that may be carried through the cable
.
.
Attenuation
This capacitance and electrical resistance of the
copper creates an impedance to signals, measured in ohms per metre (Ω/m), reducing
the strength of the signal over a long distance. This reduction is called attenuation and it
is measured in decibels (dB).
Connectors
In networking, RG-8 ‘thick’ co-axial cable is terminated
with N connectors. These bulkyconnectors
are also used with radio equipment.
RG-58 ‘thin’ co-ax is usually terminated with BNC
connectors.These are also associated with oscilloscopes, older video recorders
and radio equipment.
Twisted Pair (UTP & STP)
If pairs of plain copper wires are wrapped around each
other this helps cancel-out EMI. Twisted
pair cables offer good bandwidth but are not as good as co-axial cable. However,this kind of cabling is very cheap to
buy and install. Twisted pair comes in two flavours
UTP (unshielded twisted pair) and STP (shielded twisted pair). STP costs more but offers better electrical characteristics. The most popular kind of UTP used for networking is Category 5e (“Cat5”) cable.
UTP (unshielded twisted pair) and STP (shielded twisted pair). STP costs more but offers better electrical characteristics. The most popular kind of UTP used for networking is Category 5e (“Cat5”) cable.
Plenum cable
If you are installing a cable in an air duct, you must
use a special fire-resistant, low-smoke plenum version of the cable. Connectors
The standard connector used with Cat5 cable is the RJ45. After sorting individual wires into
appropriate channels the connector is crimped onto the wires.
Optical media
Fibre-Optic
Optical fibre transmits signals as pulses of light
along a flexible glass tube. It does not
use electricity, except to power the transmitting and receiving circuitry at
either end. Fibre optic cables have exceptional bandwidth, zero EMI and very
low attenuation and can carry signals for miles. However, they are expensive to buy and
install.
Fibre optic
cables come in two types: single-mode or multi-mode. Multi-mode cablescarry multiple signals at
once and is cheaper but can only carry signals about a mile. Single-mode cables are more expensive but are
used for long-distance (up to 24 miles).
















.jpg)






0 comments:
Post a Comment